
Stream on Hyper-heuristics
the 22nd Conference on International Federation of Operational Research Societies (IFORS 2020), June 21-26 2020, Seoul/Korea
Call for Abstracts (Max. 1500 characters)
Session 1: Selection Hyper-heuristics (Submission Code: 3298ef0c)
Session 2: Generation Hyper-heuristics (Submission Code: e964da30)
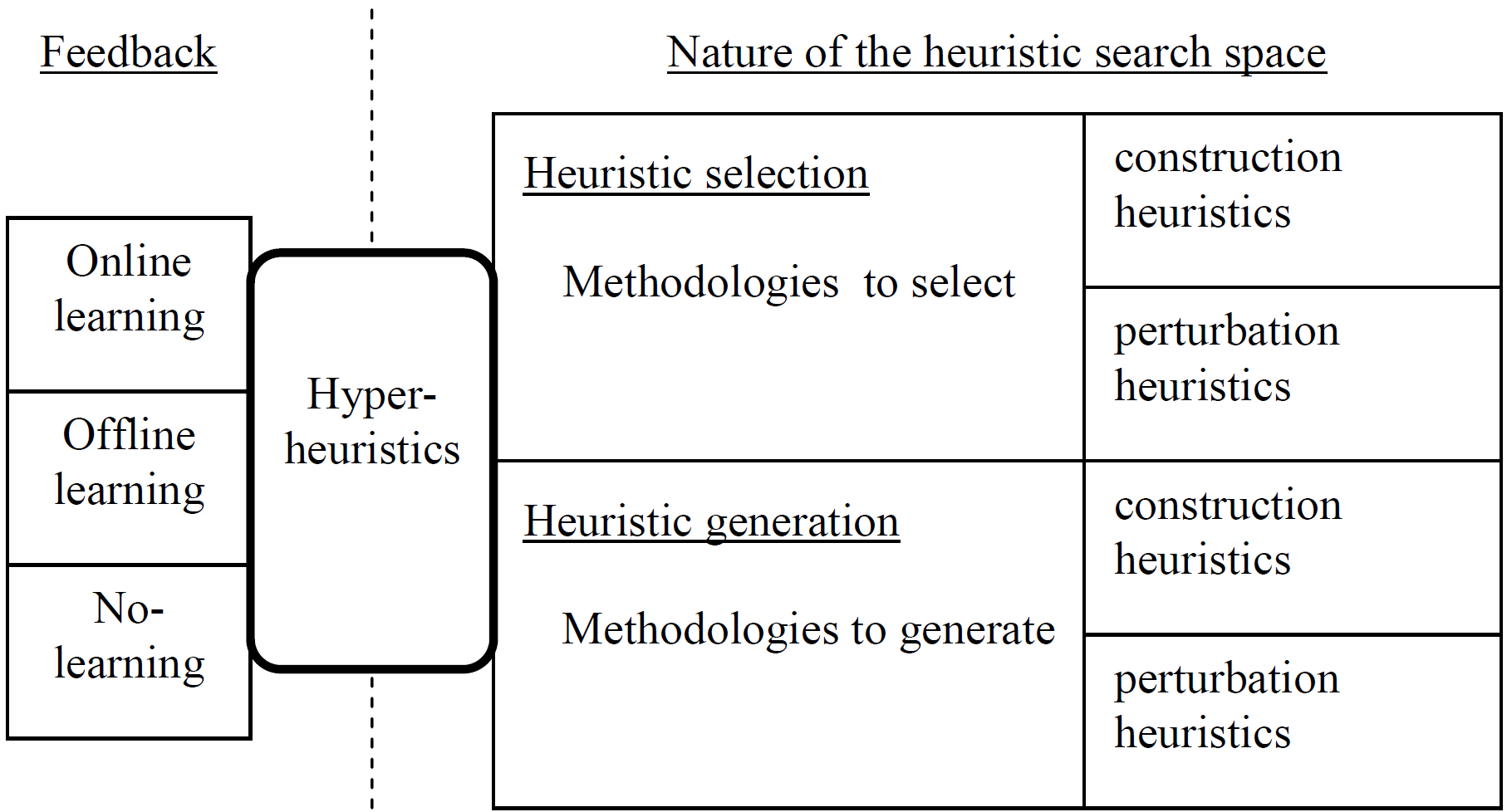
Hyper-heuristics are problem-independent generic solvers which have been successfully applied to a wide range of combinatorial search problems both from academia and real-world, such as timetabling, scheduling, routing, rostering, cutting and packing.
The studies on this field is mainly considered under two categories (Figure 1), namely Selection and Generation Hyper-heuristics.
Selection Hyper-heuristics operate by automatically choosing (low-level) heuristics from an existing heuristic set while the latter type focuses on generating heuristics from scratch based on predefined components.
These hyper-heuristics can have certain learning capabilities by incorporating Offline and Online learning.
Offline refers to learning before a hyper-heuristic run, mostly in the form of un-/supervised learning.
Online is about learning while a problem (~instance) is being solved, likely to be based on reinforcement learning.
It is also possible to design hyper-heuristics without learning.
Besides the learning aspect, the type of heuristics may differ as constructive and perturbative heuristics.
The aim of this stream is to gather researchers studying hyper-heuristics to share their research on all the aforementioned hyper-heuristic variations as well as the strategies developed to support hyper-heuristics.
This stream will be organized in connection with the Task Force on Hyper-heuristics within the Technical Committee of Intelligent Systems and Applications at the IEEE Computational Intelligence Society and IEEE Task Force on Automated Algorithm Design, Configuration and Selection (AADCS).| Important Dates |
|
Organizers
- Dr. Mustafa Misir (if any questions, contact)
Department of Computer Engineering, Istinye University, Turkey
mustafa.misir [at] istinye.edu.tr
- Prof. Nelishia Pillay
Department of Computer Science, University of Pretoria, South Africa
npillay [at] cs.up.ac.za
- Dr. Rong Qu
School of Computer Science, University of Nottingham, UK
rong.qu [at] nottingham.ac.uk