
Design and Analysis of Algorithms (COMPSCI 308)
Fall 2022-2023 / Session 2 (7 weeks, 35 hours)
Course Period: October 24 - December 8, 2022
- Lectures: Monday / Tuesday / Wednesday / Thursday @ 16:15-17:30 (Classroom: IB 1053 + Zoom)
An algorithm is any well-defined computational procedure that takes some value, or set of values, as input and produces some value, or set of values, as output. An algorithm is thus a sequence of computational steps that transform the input into the output. An algorithm can also be viewed as a tool for solving a well-specified computational problem. The statement of the problem specifies in general terms the desired input/output relationship. The algorithm describes a specific computational procedure for achieving that input/output relationship.
After having a target problem, the next step is to design an algorithm that can address the target problem. Algorithm design is a coherent discipline-one needs a specific set of concepts to define, a computational problem and a specific set of tools to design an optimal algorithm to solve it. Designing the right algorithm for a given application is a major creative act-that of taking a problem and pulling a solution out of the ether. The space of choices you can make in algorithm design is enormous, leaving you plenty of freedom.
Solely designing algorithms may not be a proper approach to solve a specific problem. Understanding their behavioral characteristics together with their strengths and weaknesses is critical. Algorithm analysis is investigated for this purpose, in particular, for determining how much of a resource, such as time or memory, an algorithm uses as a function of some characteristic of the input to the algorithm, usually the size of the input.
This course will touch all the major algorithm design and analysis steps while taking data structures into account. All the relevant concepts will be exemplified through existing algorithms and problems besides implementing algorithms in Python. To be specific, the design and analysis of efficient algorithms including sorting, searching, dynamic programming, graph algorithms, nondeterministic algorithms and computationally hard problems and other related topics will be studied.
This course will be carried out in line with the DKU's animating principles. In particular, Collaborative Problem Solving, Research and Practice and Lucid Communication will be directly involved with this course while touching the Independence and Creativity aspect. The course will be primarily executed through in-class quick quizzes, in-class individual / group discussions and weekly assignments.
By the end of this course, you will be able to:
- design efficient and effective algorithms of varying types
- implement algorithms in consideration of the problem requirements and computational resources
- utilize appropriate data structures while developing algorithms
- introduce new algorithmic solutions for new problems
- evaluate the theoretical boundaries of given algorithms
- analyze the behaviour and performance of given algorithms, referring to their strengths and weaknesses
- identify the resemblance between different problems, leading to problem hardness analysis
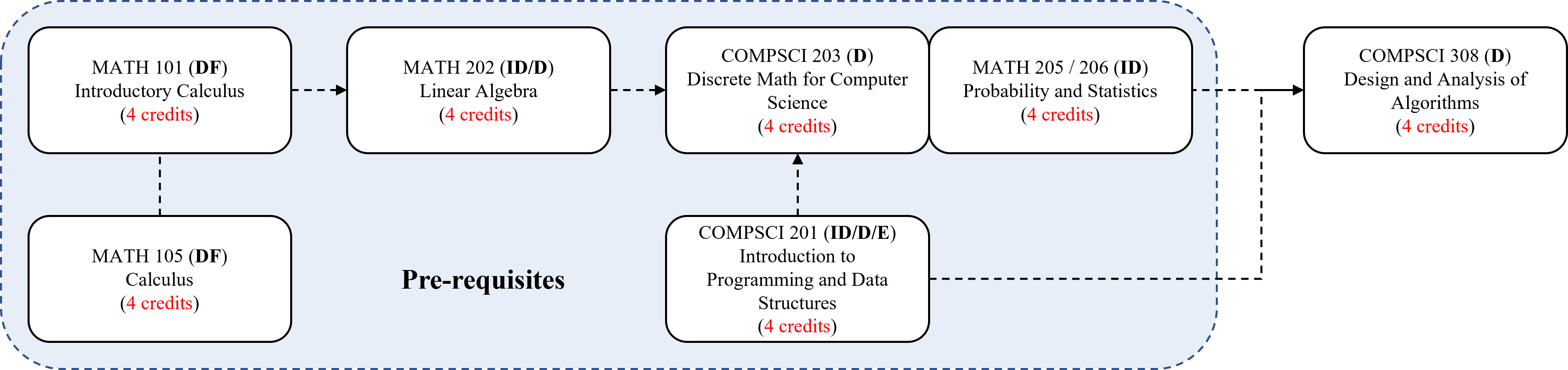
Pre-requisites
- COMPSCI 201: Introduction to Programming and Data Structures
- COMPSCI 203: Discrete Math for Computer Science or MATH 205 / 206: Probability and Statistics
Anti-requisites
- COMPSCI 301: Algorithms and Databases
The following chart shows how COMPSCI 308 fits to the DKU curriculum, where the abbreviations indicate the course types, i.e. D: Divisional, DF: Divisional Foundation, ID: Interdisciplinary and E: Elective. Refer to the DKU Undergraduate Bulletin for more details.
Reference Books
Introduction to Algorithms, Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest and Clifford Stein (3rd Edition), 2009, MIT Press (Free Book: ProQuest - Duke U.) [ Lecture Slides ]Supplementary Books:
- Algorithm Design, John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos (1st Edition), 2005, Pearson - Addison Wesley [ Lecture Slides & Examples ]
- Algorithms, Sanjoy Dasgupta, Christos Papadimitriou, Umesh Vazirani (1st Edition), 2006, McGraw-Hill
- Algorithms, Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne (4th Edition), 2011, Addison-Wesley
- Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms, Robert Sedgewick, Philippe Flajolet (2nd Edition), 2013, Addison-Wesley [ Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- The Algorithm Design Manual, Steven Skiena (3rd Edition), 2020, Springer [ Old: Lecture Slides & Videos - New: Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- Foundations of Algorithms, Richard Neapolitan (5th Edition), 2014, Jones & Bartlett Learning
- Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C++, Mark A. Weiss (4th Edition), 2014, Pearson [ Source Code in C++ ]
- Algorithm Design and Applications, Michael T. Goodrich, Roberto Tamassia (1st Edition), 2015, Wiley
- Algorithms Illuminated (Part 1): The Basics, Tim Roughgarden (1st Edition), 2017, Soundlikeyourself Publishing [ Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- Algorithms Illuminated (Part 2): Graph Algorithms and Data Structures, Tim Roughgarden (1st Edition), 2018, Soundlikeyourself Publishing [ Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- Algorithms Illuminated (Part 3): Greedy Algorithms and Dynamic Programming, Tim Roughgarden (1st Edition), 2019, Soundlikeyourself Publishing [ Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- Algorithms Illuminated (Part 4): Algorithms for NP-Hard Problems, Tim Roughgarden (1st Edition), 2020, Soundlikeyourself Publishing [ Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- Introduction to the Design and Analysis of Algorithms, Anany Levitin (3rd Edition), 2011, Addison-Wesley
- Design and Analysis of Computer Algorithms, Alfred Aho, John Hopcroft, Jeffrey Ullman (1st Edition), 1974, Addison-Wesley
- Data Structures and Algorithms, Alfred Aho, Jeffrey Ullman (1st Edition), 1983, Pearson
- Fundamentals of Computer Algorithms, Ellis Horowitz, Sartaj Sahni (1st Edition), 1984, CS Press
- A Guide to Algorithm Design: Paradigms, Methods, and Complexity Analysis, Anne Benoit, Yves Robert, Frederic Vivien (1st Edition), 2014, CRC
- Algorithms: Sequential, Parallel, and Distributed, Kenneth A. Berman, Jerome L. Paul (1st Edition), 2004, Course Technology
- The Design and Analysis of Algorithms, Dexter C. Kozen (1st Edition), 1992, Springer
- Algorithms, Jeff Erickson (1st Edition), 2019 (Free Book)
- The Design of Approximation Algorithms, David P. Williamson, David B. Shmoys (1st Edition), 2011, Cambridge University (Free Book)
- Approximation Algorithms, Vijay V. Vazirani (1st Edition), 2003, Springer
- Introduction to the Theory of Computation, Michael Sipser (3rd Edition), 2013, Cengage
- What Can Be Computed?: A Practical Guide to the Theory of Computation, John MacCormick (1st Edition), 2018, Princeton University
- Computational Complexity: A Modern Approach, Sanjeev Arora, Boaz Barak (1st Edition), 2009, Cambridge University (Free Draft)
- Mathematics and Computation: A Theory Revolutionizing Technology and Science, Avi Wigderson (1st Edition), 2019, Princeton University (Free Draft)
- Algorithms and Complexity, Herbert S. Wilf (2nd Edition), 2002, CRC
- Complexity Theory: Exploring the Limits of Efficient Algorithms, Ingo Wegener (1st Edition), 2005, Springer
- Automata, Computability and Complexity: Theory and Applications, Elaine A. Rich (1st Edition), 2007, Pearson (Free Book)
- Data Structures and Algorithms in Python, Michael T. Goodrich, Roberto Tamassia, Michael H. Goldwasser (1st Edition), 2013, Wiley
- Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Structures using Python, Brad Miller and David Ranum, Franklin (2nd Edition), 2011, Beedle & Associates (Free Book)
- Think Complexity, Allen B. Downey (2nd Edition), 2016 / 2018, Green Tea Press / O'Reilly Press (Free Book) [ Source Code in Python ]
- Dive Into Algorithms: A Pythonic Adventure for the Intrepid Beginner, Bradford Tuckfield (1st Edition), 2021, No Starch Press
- Algorithms in a Nutshell: A Practical Guide, George T. Heineman, Gary Pollice, Stanley Selkow (2nd Edition), 2016, O'Reilly Press (Partially Python)
- A Common-Sense Guide to Data Structures and Algorithms: Level Up Your Core Programming Skills, Jay Wengrow (2nd Edition), 2020, Pragmatic Bookshelf [ Source Code in Python, Ruby and JavaScript ]
Lecture Notes / Slides
- Week 0 (Reviews)
- Python Programming
- External Lecture Slides / Videos / Book: Python for Everybody by Charles R. Severance
- External Course: 6.0001 (MIT) - Introduction to Computer Science and Programming in Python by Ana Bell, Eric Grimson, John Guttag [ Fall 2016: Lecture Videos ]
- External Course: CS50 (Harvard U.) - Introduction to Computer Science by David J. Malan [ Fall 2022 (Week 6): Lecture Video ]
- Data Structures
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 10: Elementary Data Structures
- Discrete Mathematics
- External Course: 6.042J (MIT) - Mathematics for Computer Science by Albert R. Meyer [ Fall 2015: Lecture Videos, Free Textbook ]
- Week 1 [24/10 - 27/10] (Keywords: History, Terminology and Basics; Algorithms; Computation; Asymptotic Notations)
- About COMPSCI 308
- Lecture Slides: L1-0: About COMPSCI 308
- Introduction to Algorithms
- Lecture Slides: L1-1: Introduction to Algorithms
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 1: The Role of Algorithms in Computing
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 2: Getting Started
- External Lecture Notes: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Jason Ku, and Justin Solomon (Spring 2020) - Algorithms and Computation
- External Recitation Notes: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Jason Ku, and Justin Solomon (Spring 2020) - Introduction and Asymptotics
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Jason Ku (Spring 2020) - Algorithms and Computation
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas (Fall 2011) - Algorithmic Thinking, Peak Finding
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas (Fall 2011) - Models of Computation, Python Cost Model, Document Distance
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine (Spring 2020) - Data Structures and Dynamic Arrays
- Asymptotic Notations
- Lecture Slides: L1-2: Asymptotic Notations
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 3: Growth of Functions
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 2: Basics of Algorithm Analysis
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 1.4: Analysis of Algorithms
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine (Spring 2020) - Data Structures and Dynamic Arrays
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Justin Solomon (Spring 2020) - Sets and Sorting
- Week 2 [31/10 - 03/11] (Keywords: Divide and Conquer; Dynamic Programming)
- Divide and Conquer
- Lecture Slides: L2-1: Divide and Conquer
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 4: Divide and Conquer
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 5: Divide and Conquer
- Dynamic Programming
- Lecture Slides: L2-2: Dynamic Programming
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 15: Dynamic Programming
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 6: Dynamic Programming
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine (Spring 2020) - Dynamic Programming: Part 1, Part 2, Part 3, Part 4
- Week 3 [07/11 - 10/11] (Keywords: Greedy Algorithms; Graphs; Graph Algorithms)
- Greedy Algorithms
- Lecture Slides: L3-1: Greedy Algorithms
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 16: Greedy Algorithms
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 4: Greedy Algorithms
- Graph Algorithms
- Lecture Slides: L3-2: Graph Algorithms
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 3: Graphs
- External Lecture Notes: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Jason Ku, and Justin Solomon (Spring 2020) - Breadth-First Search (BFS), Depth-First Search (DFS)
- External Recitation Notes: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Jason Ku, and Justin Solomon (Spring 2020) - Breadth-First Search (BFS), Depth-First Search (DFS)
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas (Fall 2011) - Breadth-First Search (BFS), Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Week 4 [14/11 - 17/11] (Keywords: Minimum Spanning Trees; Shortest Path Algorithms)
- Minimum Spanning Trees
- Lecture Slides: L4-1: Minimum Spanning Trees
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 23: Minimum Spanning Trees
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 4.5: The Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 4.3: Minimum Spanning Trees
- Shortest Path Algorithms
- Lecture Slides: L4-2: Shortest Path Algorithms
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 22: Single-Source Shortest Paths, Chapter 23: All-Pairs Shortest Paths
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 4.4: Shortest Paths in a Graph
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 4.4: Shortest Paths
- Week 5 [21/11 - 24/11] (Keywords: Optimization; Mathematical Modelling; Linear Programming; Duality; Maximum Flow)
- Linear Programming
- Lecture Slides: L5-1: Linear Programming
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 29: Linear Programming
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 11.6: Linear Programming and Rounding
- Duality
- Lecture Slides: L5-2: Duality
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 29.4: Duality
- Maximum Flow
- Lecture Slides: L5-3: Maximum Flow
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 26: Maximum Flow
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 7: Network Flow
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 6.4: Maximum Flow
- Week 6 [28/11 - 01/12] (Keywords: Randomized Algorithms, Hash Tables)
- Randomized Algorithms
- Lecture Slides: L6-1: Randomized Algorithms
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 5.3: Randomized Algorithms
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 13: Randomized Algorithms
- Hash Tables
- Lecture Slides: L6-2: Hash Tables
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 11: Hash Tables
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 13.6: Hashing
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 3.4: Hash Tables
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Jason Ku (Spring 2020) - Hashing
- Week 7 [05/12 - 08/12] (Keywords: P; NP; NP-Completeness; Approximation Algorithms)
- P and NP
- Lecture Slides: L7-1: P and NP
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 34: NP-Completeness (34.1, 34.2)
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 8: NP and Computational Intractability (8.1, 8.2, 8.3)
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 6: Intractability
- External Lecture Videos: Introduction to Algorithms: 6.006 (MIT) by Erik Demaine (Spring 2020) - Complexity
- NP-Completeness
- Lecture Slides: L7-2: NP-Completeness
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 34: NP-Completeness (34.3, 34.4, 34.5)
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 8: NP and Computational Intractability
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithms by Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne - Chapter 6: Intractability
- Approximation Algorithms
- Lecture Slides: L7-3: Approximation Algorithms
- Book Chapter: Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas Cormen et al. - Chapter 35: Approximation Algorithms
- Book Chapter (Optional): Algorithm Design by John Kleinberg, Eva Tardos - Chapter 11: Approximation Algorithms
Grading
- Homework Assignments: 20%
- Mathematical, Conceptual, or Programming related
- Submit on Sakai; 7 in total
- Quizzes: 10%
- Weekly Journals: 10%
- Each week, write a page or so about what you have learned
- Submit on Sakai; 2 points off for each missing journal, capped at 10
- Midterm: 25%
- Final: 35%
Reference Courses
- 6.006: Introduction to Algorithms (MIT) [ Fall 2011 by Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas: Lecture Slides & Videos; Spring 2020 by Erik Demaine, Jason Ku, Justin Solomon: Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms by Rong Ge (Duke U.) [ Spring 2020: Lecture Slides ]
- CSE 373: Analysis of Algorithms by Steven Skiena (Stony Brook U.) [ Fall 2020/2021: Lecture Slides & Videos ]
- COS 423: Theory of Algorithms by Kevin Wayne (Princeton U.) [ Spring 2018: Lecture Slides ]
- CIS 320: Introduction to Algorithms by Aaron Roth (U. Penn) [ Fall 2021: Lecture Notes ]
- CS 4820: Introduction to Analysis of Algorithms by Robert David (Bobby) Kleinberg (Cornell U.) [ Spring 2021: Lecture Notes ]
- CS 125: Algorithms & Complexity by Jelani Nelson (Harvard U.) [ Fall 2016: Lecture Notes ]
- CS 120: Introduction to Algorithms and their Limitations by Salil Vadhan (Harvard U.) [ Fall 2021: Lecture Notes ]
Other Books
Quick / Easy Reads:- Grokking Algorithms: An Illustrated Guide for Programmers and Other Curious People, Aditya Bhargava (1st Edition), 2018, Manning
- Algorithms Unlocked, Thomas H. Cormen (1st Edition), 2013, MIT Press
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human Decisions, Brian Christian, Tom Griffiths (1st Edition), 2016, Henry Holt and Co. [ Video Lecture ]
- Algorithms, Panos Louridas (1st Edition), 2020, MIT Press
- Real-World Algorithms: A Beginner's Guide, Panos Louridas (1st Edition), 2017, MIT Press
- Nine Algorithms that Changed the Future: the Ingenious Ideas that Drive Today's Computers, John MacCormick (1st Edition), 2012, Princeton University Press
- What Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of Computing, Ed Finn (1st Edition), 2017, MIT Press
- Introducing Python for Computer Science and Data Scientists, Paul Deitel, Harvey Deitel (1st Edition), 2020, Pearson
- Introduction to Computation and Programming Using Python: With Application to Computational Modeling and Understanding Data, John V. Guttag (3rd Edition), 2021, MIT Press
- Think Python: How to Think Like a Computer Scientist, Allen B. Downey (2nd Edition), 2016, O'Reilly Press (Free Book)
- How to Think Like a Computer Scientist: Learning with Python 3, Peter Wentworth, Jeffrey Elkner, Allen B. Downey, Chris Meyers (3rd Edition), 2012 (Free Book)
- A Programmer's Guide to Computer Science (Vol. 1), William M. Springer II (1st Edition), 2019, Jaxson Media
- A Programmer's Guide to Computer Science (Vol. 2), William M. Springer II (1st Edition), 2020, Jaxson Media
- A Byte of Python, Swaroop C. H. (4th Edition), 2016 (Free Book)
- Project Python, Devin Balkcom, 2011 (Free Book)
- Python for Everybody: Exploring Data in Python 3, Charles Severance, 2016 (Free Book)
- Automate The Boring Stuff With Python, Al Sweigart (2nd Edition), 2019, No Starch Press (Free Book)
- Beyond the Basic Stuff with Python, Al Sweigart (1st Edition), 2020, No Starch Press (Free Book)
- Python Programming in Context, Bradley N. Miller, David L. Ranum, Julie Anderson (3rd Edition), 2019, Jones & Bartlett Learning
- Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science, John Zelle (3rd Edition), 2016, Franklin, Beedle & Associates
- A Hands-On, Project-Based Introduction to Programming, Eric Matthes (2nd Edition), 2016, No Starch Press (Free Book)
- Learn Python 3 the Hard Way, Zed A. Shaw (1st Edition), 2017, Addison-Wesley
- Introducing Python: Modern Computing in Simple Packages, Bill Lubanovic (2nd Edition), 2019, O'Reilly Press
- Clean Code in Python: Develop Maintainable and Efficient Code, Mariano Anaya (2nd Edition), 2021, Packt
- The Self-Taught Computer Scientist: The Beginner's Guide to Data Structures & Algorithms, Cory Althoff (1st Edition), 2021, Wiley
- The Big Book of Small Python Projects: 81 Easy Practice Programs, Al Sweigart (1st Edition), 2021, No Starch Press (Free Book)
- Invent Your Own Computer Games with Python, Al Sweigart (4th Edition), 2016, No Starch Press (Free Book)
- Cracking Codes with Python: An Introduction to Building and Breaking Ciphers, Al Sweigart (1st Edition), 2018, No Starch Press (Free Book)
- Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science, Ronald L. Graham, Donald E. Knuth, Oren Patashnik (2nd Edition), 1994, Addison-Wesley
- Mathematics for Computer Science, Eric Lehman, F. Thomson Leighton, Albert R. Meyer (1st Edition), 2017 (2018R), Samurai Media (Free Book) [ 6.042: Mathematics for Computer Science (MIT) - Materials ]
- Mathematics: A Discrete Introduction, Edward A. Scheinerman (3rd Edition), 2012, Cengage Learning
- Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, Kenneth H. Rosen (8th Edition), 2019, McGraw-Hill
- Discrete Mathematics: An Open Introduction, Oscar Levin (3rd Edition), 2021 (Free Book)
- Essential Discrete Mathematics for Computer Science, Harry Lewis, Rachel Zax (1st Edition), 2019, Princeton University
- Connecting Discrete Mathematics and Computer Science, David Liben-Nowell (1st Edition), 2022, Cambridge University Press
- Book of Proof, Richard H. Hammack (3rd Edition), 2018 (Free Book)
- Applied Combinatorics, Mitchel T. Keller, William T. Trotter (3rd Edition), 2021 (Free Book)
- A Decade of the Berkeley Math Circle: The American Experience (Volume 1, Volume 2), Zvezdelina Stankova, Tom Rike (Eds), 2008, American Mathematical Society
- How to Think Like a Mathematician: A Companion to Undergraduate Mathematics, Kevin Houston (1st Edition), 2009, Cambridge University Press
- The Art of Problem Solving (Vol. 2): And Beyond, Richard Rusczyk, Sandor Lehoczky (7th Edition), 2006, AoPS Incorporated
- The Art of Problem Solving (Vol. 1), Sandor Lehoczky, Richard Rusczyk (7th Edition), 2006, AoPS Incorporated
- What Is Mathematics? An Elementary Approach to Ideas and Methods, Richard Courant, Herbert Robbins (2nd Edition), 1996, Oxford University Press
Other Materials / Resources
Cheat Sheets:- Algorithms and Data Structures Cheat Sheet from Algorithms (4th Ed.) by Robert Sedgewick (Princeton U.) and Kevin Wayne (Princeton U.)
- The Asymptotic Cheat Sheet by Tom Leighton (MIT) and Ronitt Rubinfeld (MIT)
- Big-O Cheat Sheet by Cameron Musco (UMass Amherst)
- VISUALALGO: Visualising Data Structures and Algorithms through Animation
- Visualizing Algorithms by Mike Bostock
- Sorting Algorithms Animations
- Data Structure and Algorithm Visualizations by David Galles (U. San Francisco)
- Algorithm Visualizer by Jason Park
- Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures by NIST, US
- An overview of Python Data Visualization libraries
- Philip W. L. Fong, 2009. Reading a Computer Science research paper. ACM SIGCSE Bulletin, 41(2), pp.138-140
- You and Your Research by Richard Hamming (Bell Labs / NPS). Bell Communications Research Colloquium Seminar, 7 March 1986
- An Online LaTeX Editor: Overleaf
- LaTeX Tutorial (Overleaf): Learn LaTeX in 30 minutes
- The Not So Short Introduction to LaTeX by Tobias Oetiker, Hubert Partl, Irene Hyna, Elisabeth Schlegl, 2021
- How To Speak / Present (Video) by Patrick Winston (MIT)